Simulation Lab
Overview
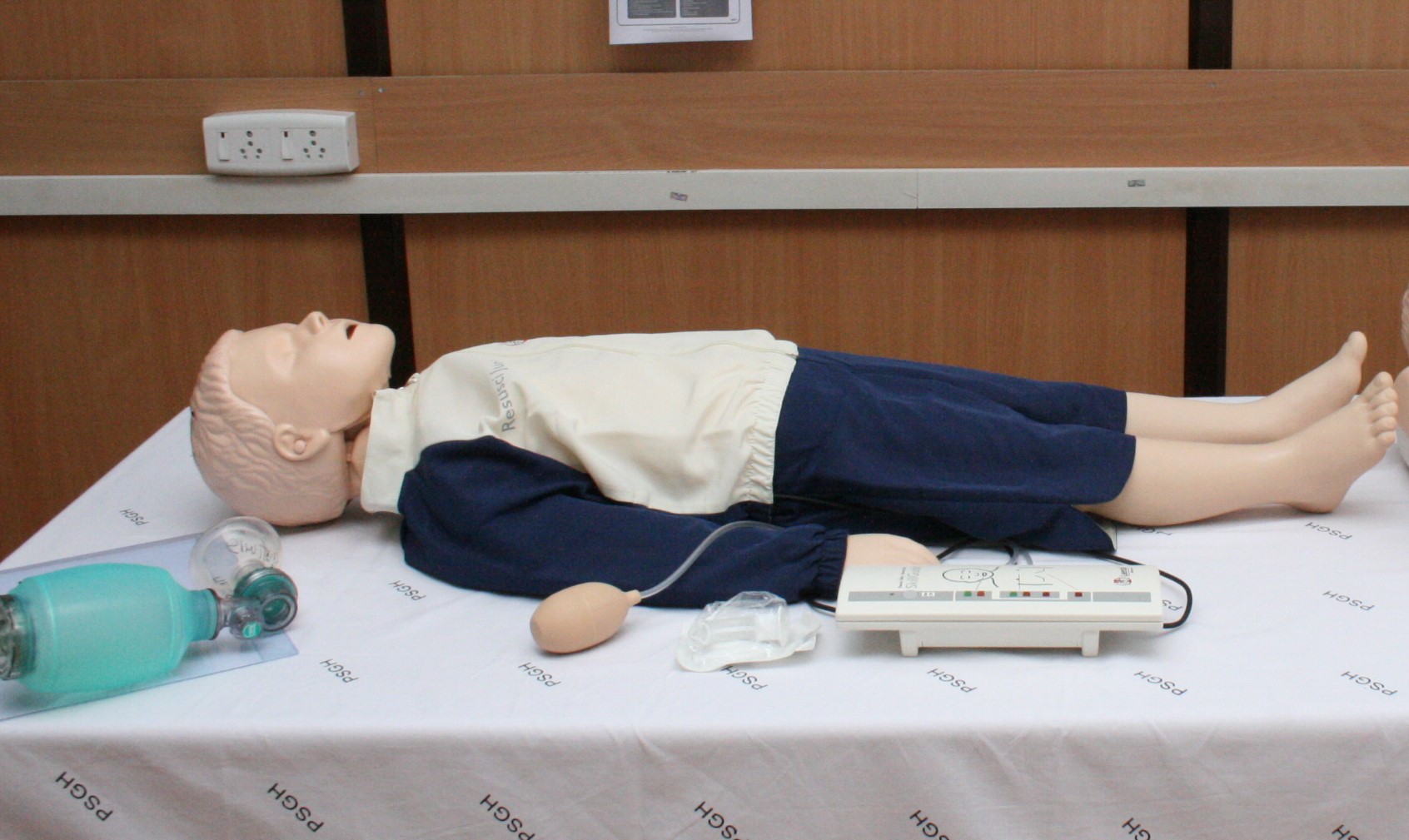
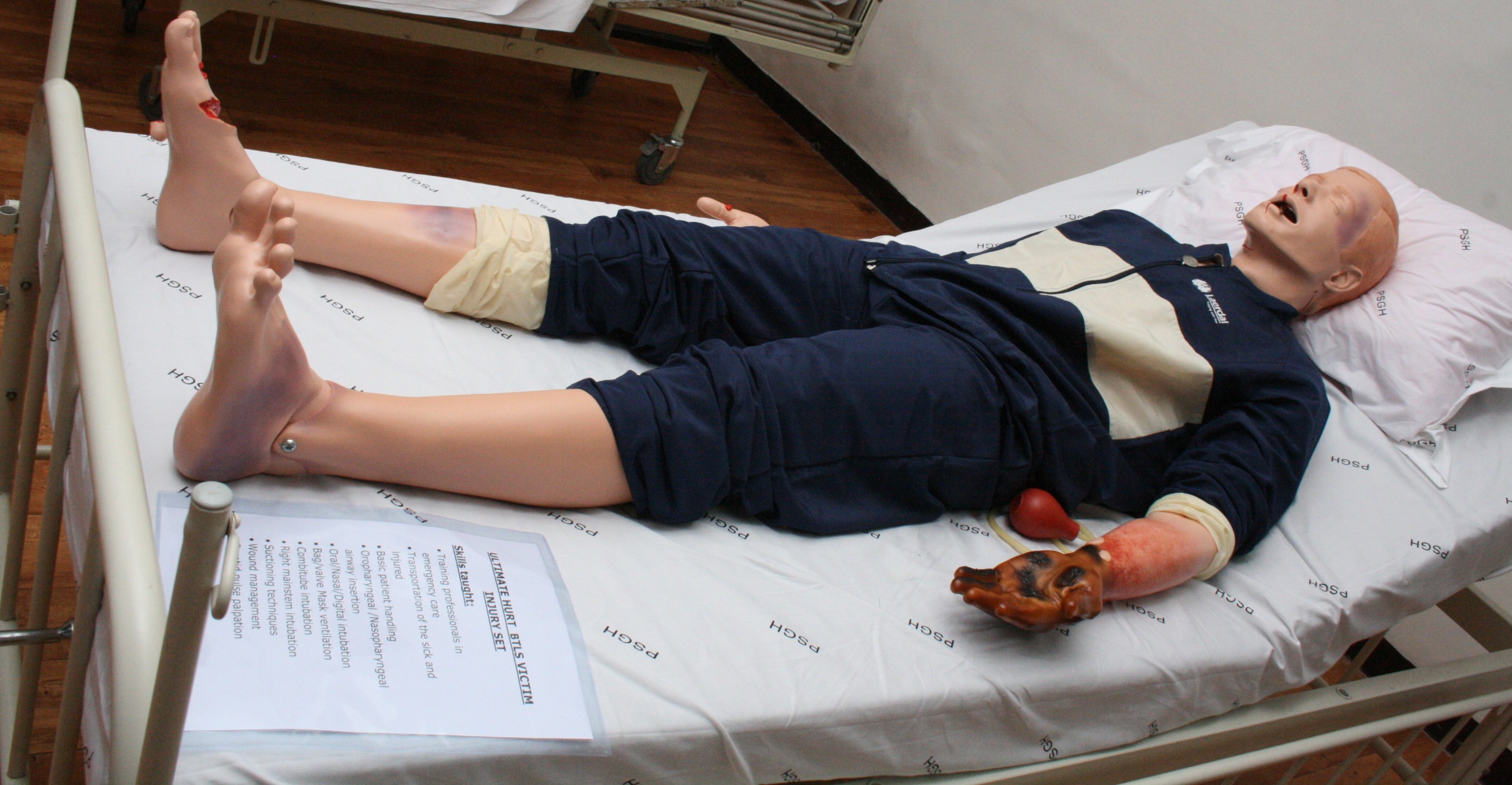
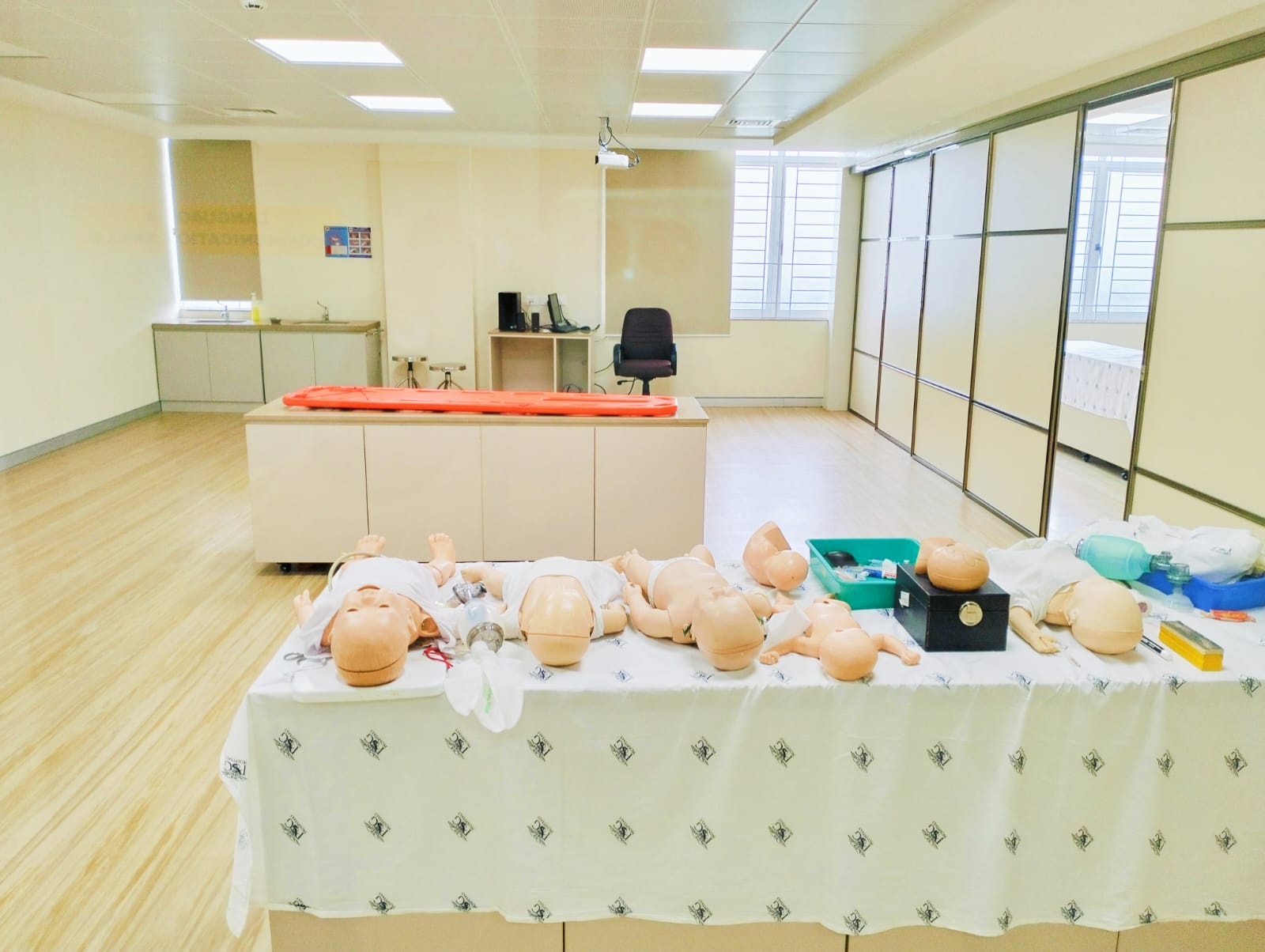
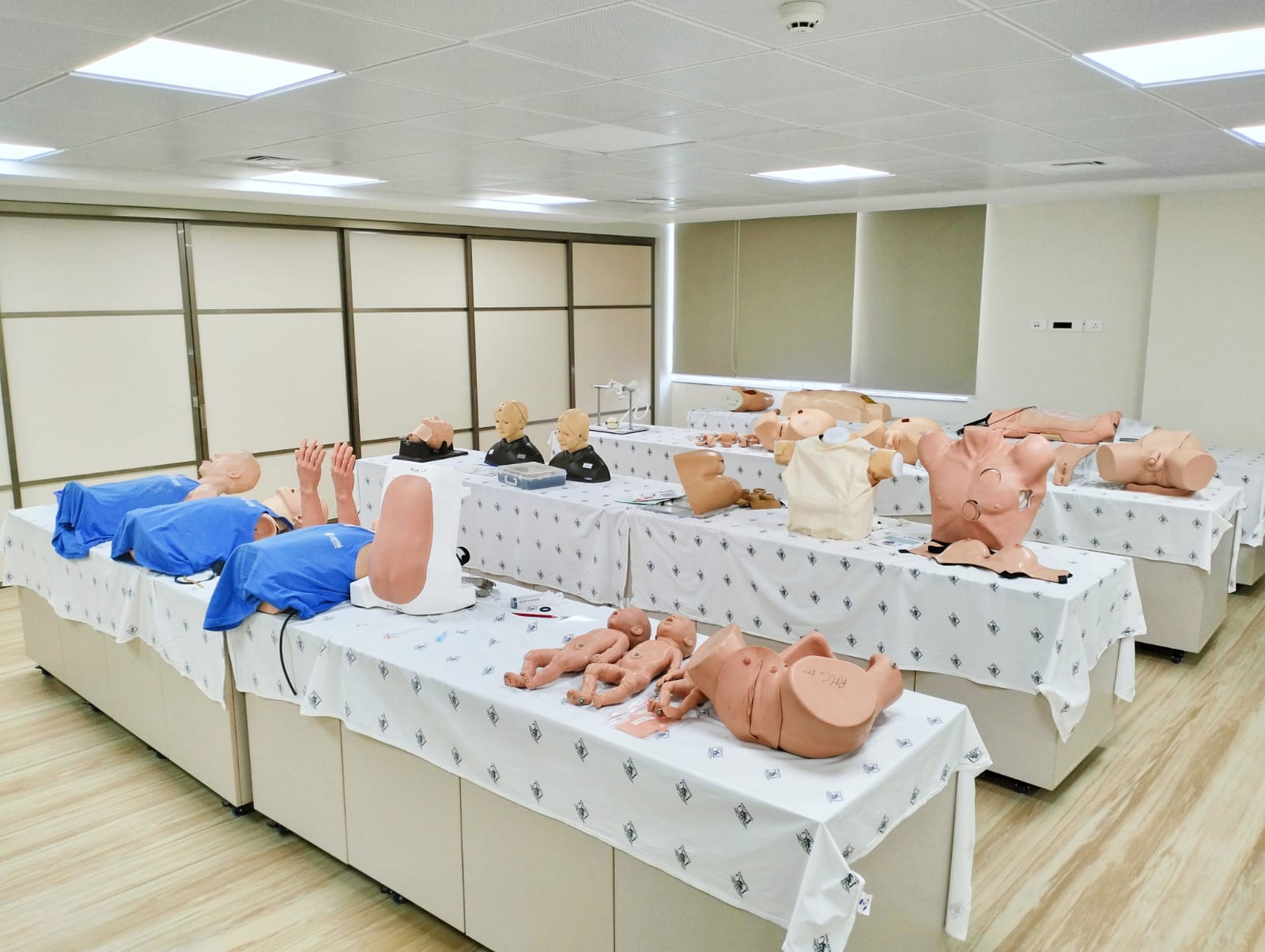
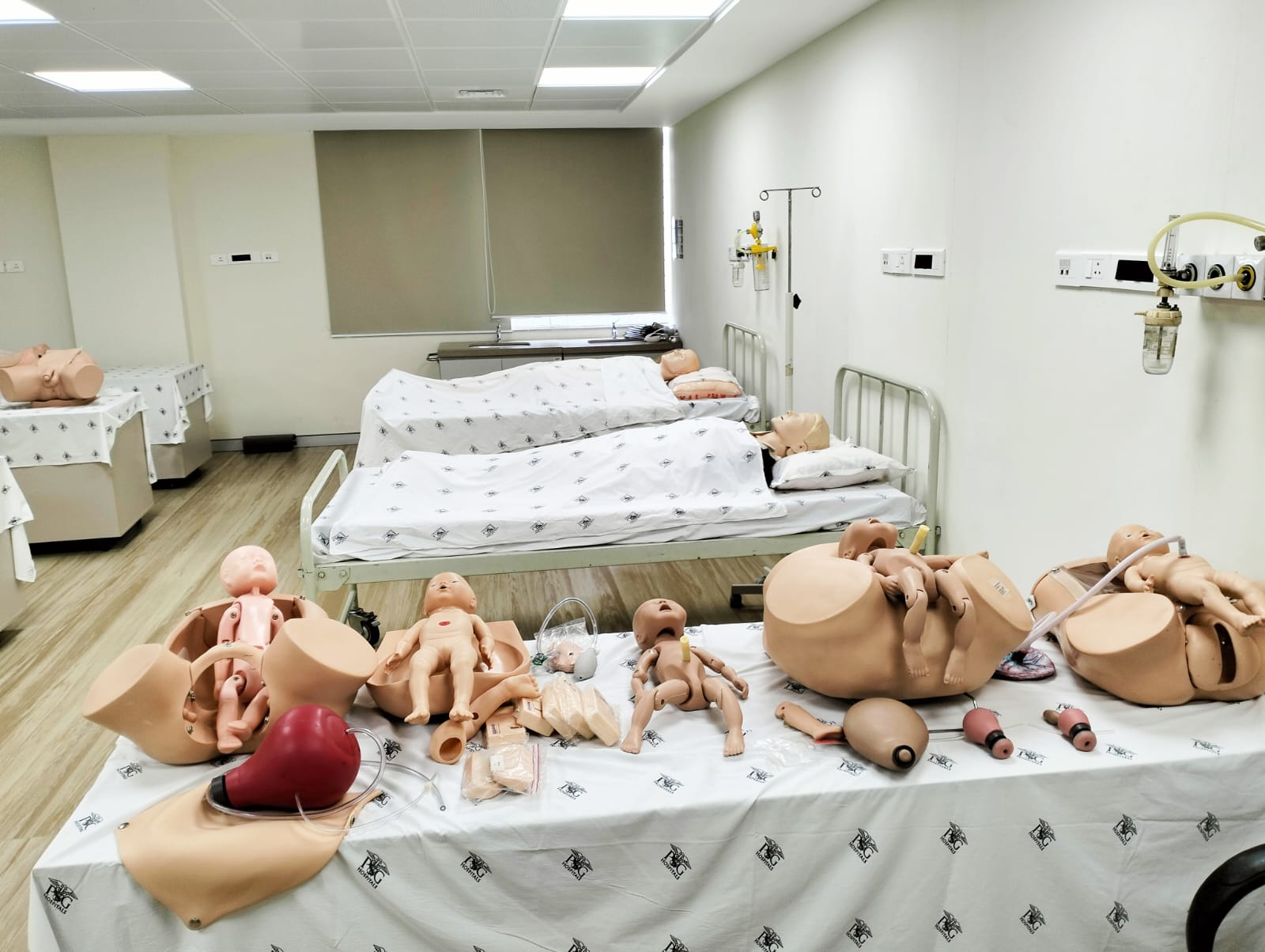
The simulation lab at PSG Institute of Medical Sciences & Research is a specialized facility designed to simulate clinical scenarios and provide hands-on training to medical students, residents, and healthcare professionals. The center has a range of more than 100 training manikins, from simple task trainers to the most complex, interactive, computer-based training units such as the SimMan™.It is a recognized center by the American Heart Association and conducts regular training programs on AHA Basic and Advanced Life Support.
Here’s an overview of what you might find in a simulation lab within our Facility:
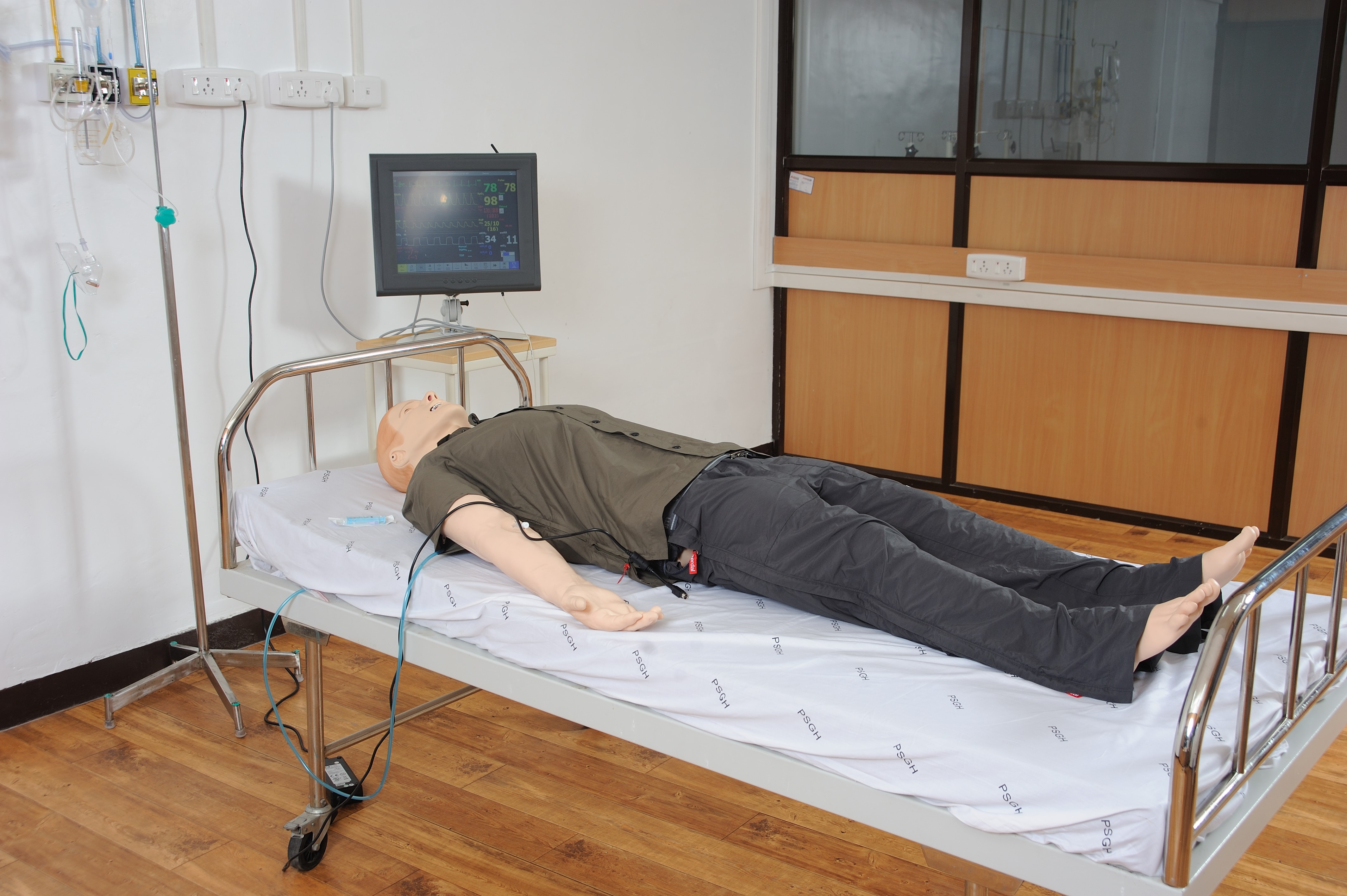
Patient Simulators:
These are high-fidelity manikins that replicate various physiological responses and can simulate a wide range of medical conditions. They often feature realistic vital signs, breathing patterns, heart sounds, and can respond to interventions such as medication administration, CPR, or medical procedures.
Contact Information
Email id:
simulationlab@psgimsr.ac.in-
Contact Number:
+91 9894769988
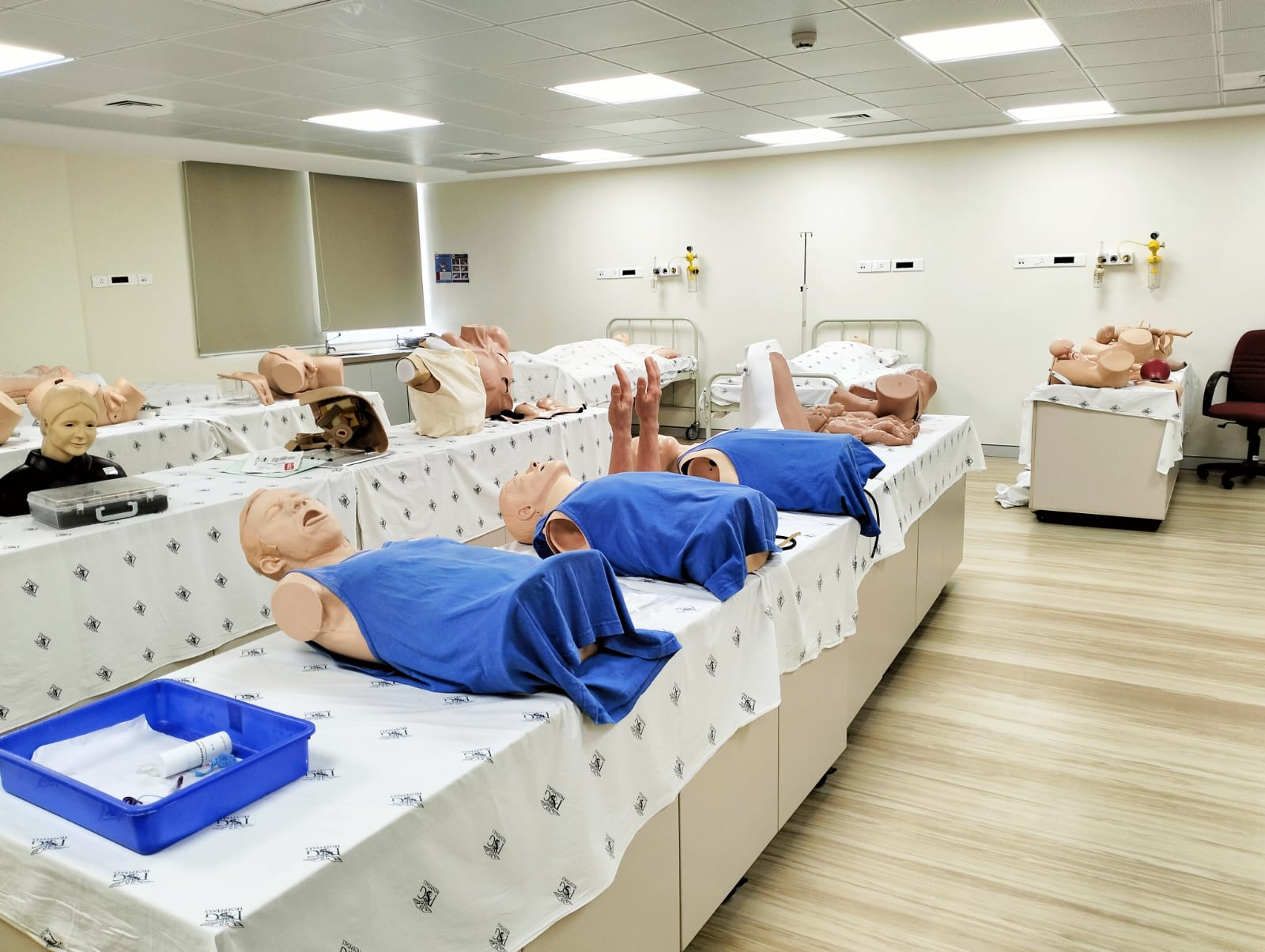
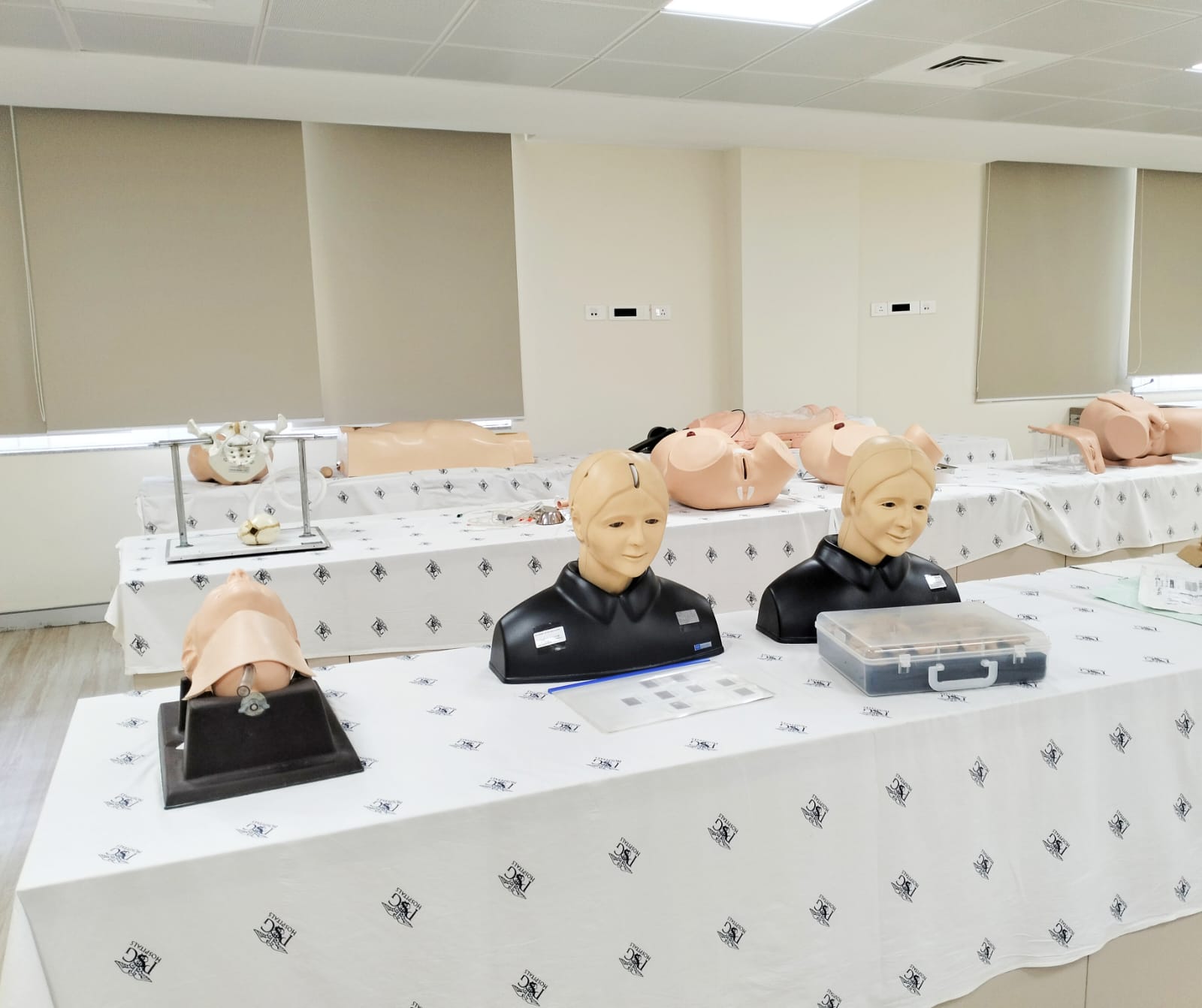
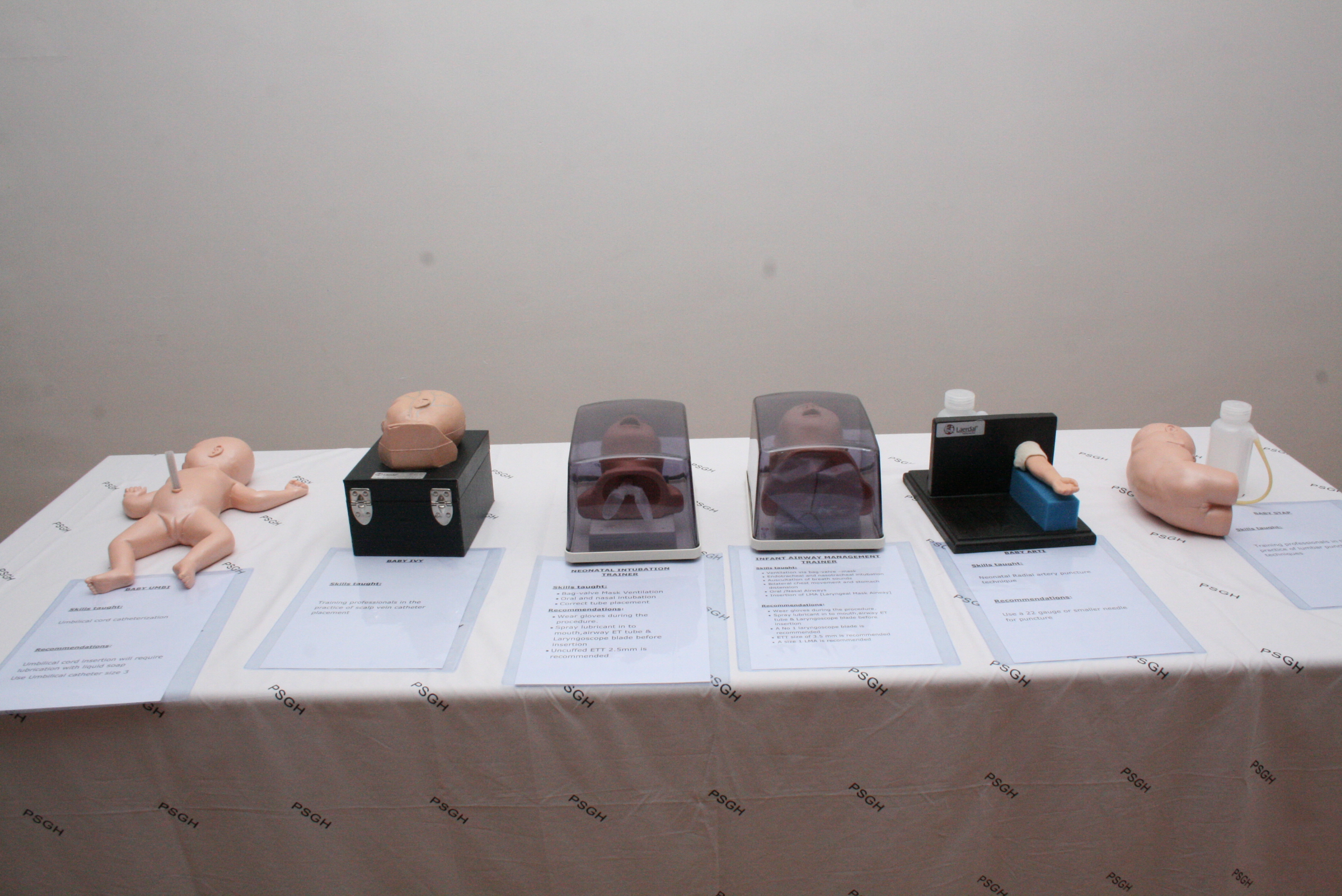




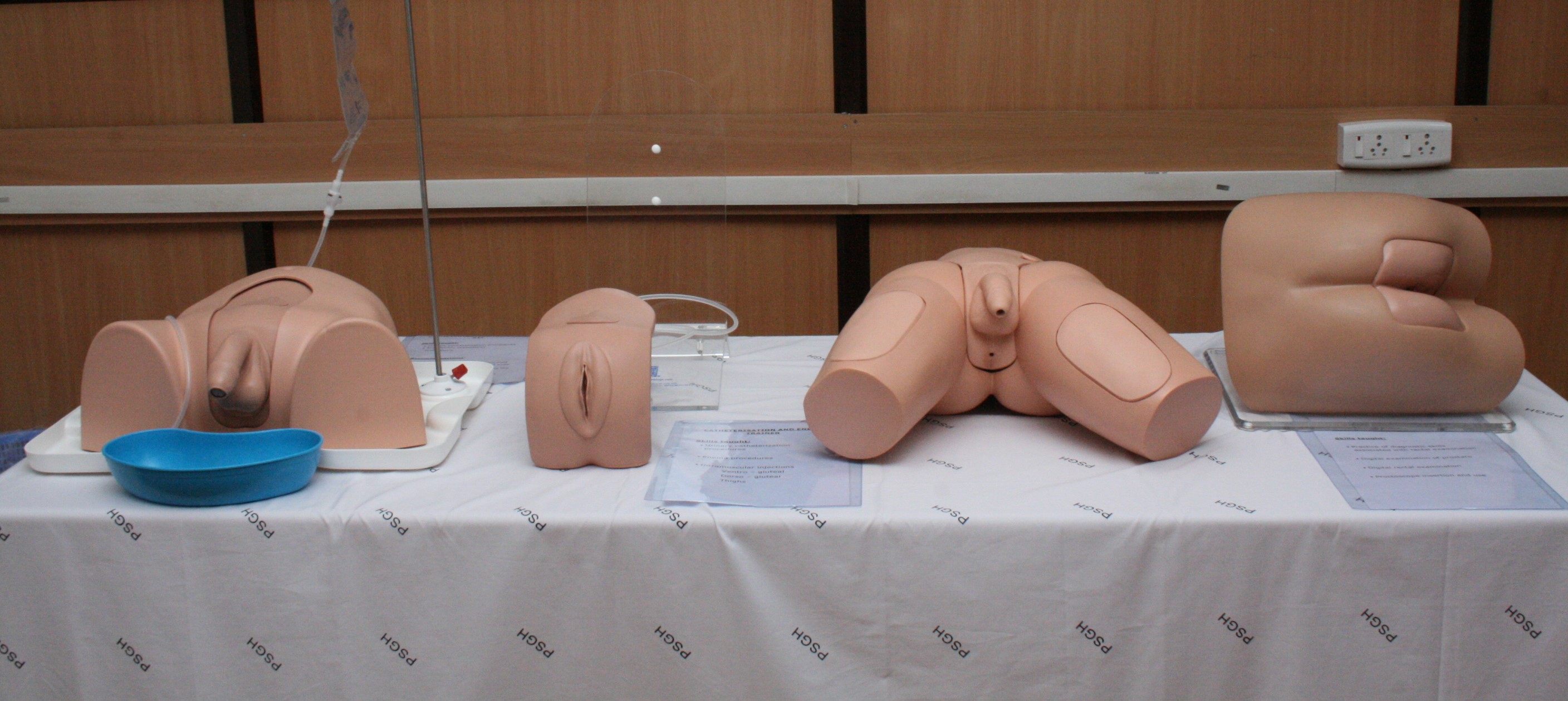

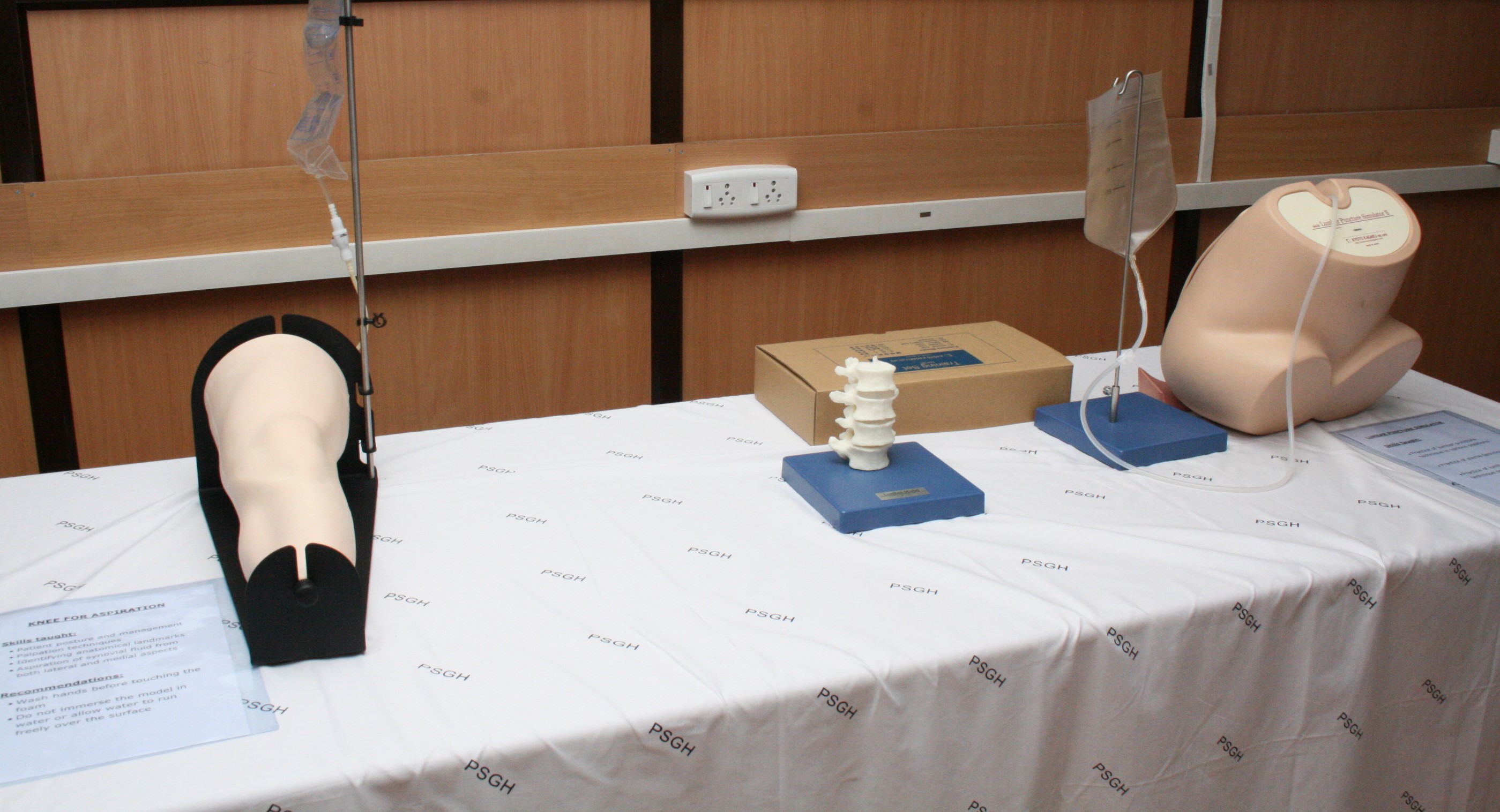
Task Trainers:
Task trainers are simulation devices designed to teach specific skills or procedures. For example, there might be task trainers for suturing, central line insertion, lumbar puncture, or airway management. These trainers allow learners to practice skills in a controlled environment before performing them on real patients.
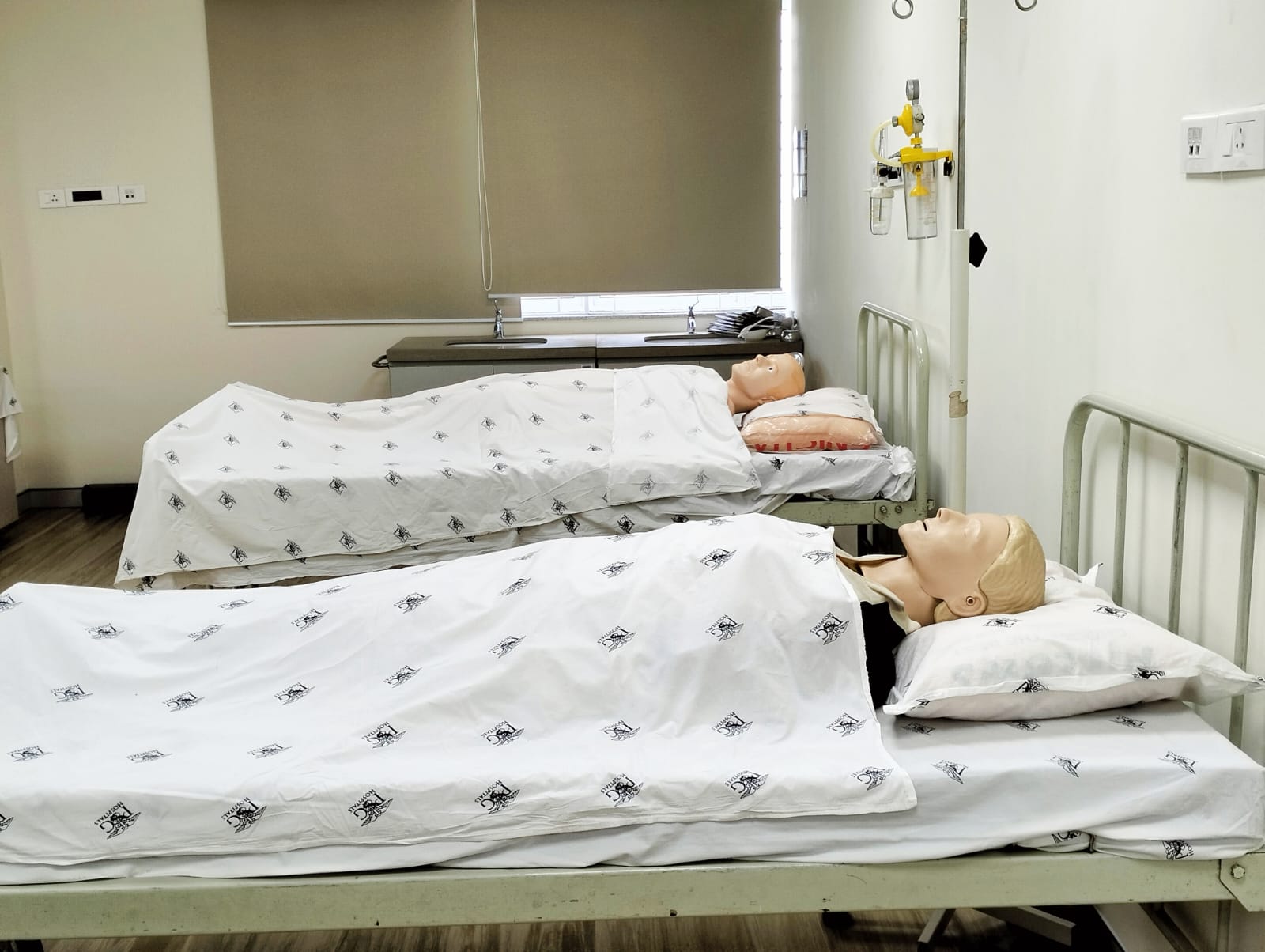
Simulated Environments:
Simulation labs may feature mock clinical environments such as hospital rooms, operating rooms, intensive care units, or emergency departments. These environments are equipped with medical equipment, monitors, and supplies to create a realistic setting for simulation scenarios.
Standardized Patients:
Some simulation labs utilize standardized patients, who are trained actors or individuals trained to portray specific medical conditions or scenarios. Standardized patients interact with learners, providing an opportunity for history-taking, physical examination, communication skills practice, and bedside manner development.
Debriefing Rooms:
Debriefing is a crucial component of simulation-based learning. Simulation labs typically have dedicated debriefing rooms equipped with audiovisual recording equipment. Debriefing sessions allow participants to review their performance, receive feedback from instructors, and discuss their experiences and decision-making processes.
Interdisciplinary Training:
Simulation labs in medical colleges often facilitate interdisciplinary training, bringing together medical students, nursing students, pharmacy students, and other healthcare professionals to collaborate on complex patient care scenarios.
Research and Development:
Medical simulation labs also serve as hubs for research and development in medical education. Researchers may investigate the effectiveness of simulation-based training, develop new simulation technologies, or study human factors and team dynamics in healthcare settings.
Overall, simulation labs in PSIMS&R play a vital role in medical education by providing a safe and immersive environment for learners to develop clinical skills, improve patient care, and enhance teamwork and communication abilities.
Skills Lab
PSGIMSR Skills Lab Facility , provides medical undergraduate and post-graduate students resources to practice and improve skills as per the specified NMC competency-based undergraduate medical curriculum. By utilizing manikins and trainers with varying levels of complexity and fidelity, the skills lab offers a realistic and safe learning environment for students. This hands-on approach allows students to observe, learn, and practice skills effectively. Students have the opportunity to observe demonstrations and practice skills repeatedly until they achieve proficiency. This iterative process fosters skill acquisition and confidence among students.